Lordosis is a condition where there is an increased inner curvature of the spine in lumbar region and cervical region of the human spine. Lordosis refers to your natural lordotic curve, which is normal. But if your curve arches too far inward, it’s called lordosis, or swayback. Lordosis can affect your lower back and neck. This can lead to excess pressure on the spine, causing pain and discomfort.
It can affect your ability to move if it’s severe and left untreated.It can affect your ability to move if it’s severe and left untreated.The normal outward (convex) curvature in the thoracic and sacral regions is termed kyphosis or kyphotic. The term comes from the Greek lordōsis, from lordos (“bent backward”).
Hyperlordosis also known as a anterior pelvic tilt.
Anatomy Of Cervical, Thoracic And Lumbar Spine :
To understand lordosis, we must understand normal spine anatomy. The normal anatomy of the spine is usually described by dividing up the spine into three major sections:
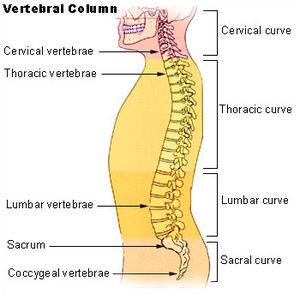
ANATOMY OF SPINE – VERTEBRAE
the cervical : There are 7 cervical vertebrae
the thoracic : 12 thoracic vertebrae
the lumbar spine : 5 lumbar vertebrae.
(Below the lumbar spine is a bone called the sacrum, which is part of the pelvis).
Each section is made up of individual bones, called vertebrae.
The normal spine has an S-shaped curve when viewed from the side. This shape allows for an even distribution of weight and flexibility of movement. The spine curves in the following ways :
The cervical spine curves slightly inward, sometimes described as a backward C-shape or lordotic curve.
The thoracic spine curves outward, forming a regular C-shape with the opening at the front—or a kyphotic curve.
The lumbar spine curves inward and, like the cervical spine, has a lordotic or backward C-shape.
The curves of the spine can be exaggerated in any plane, leading to pain, deformity and neurologic dysfunction. Some abnormal curves are asymptomatic while other require treatment.
Common Postural-Spinal Deviation is Kyphosis, Scoliosis,Lordosis,Flat Back.
What are the types of lordosis ?
Lordosis in the lower back :
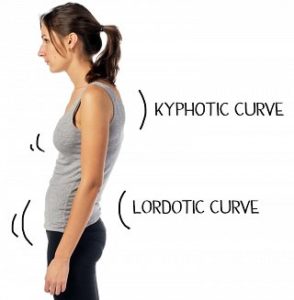
LORDOSIS -POSTURE
- Lordosis in the lower back, or lumbar spine, is the most common type. The easiest way to check for this condition is to lie on your back on a flat surface. You should be able to slide your hand under your lower back, with little space to spare.
- Someone with lordosis will have extra space between their back and the surface. If they have an extreme curve, there’ll be a visible C-like arch when they stand. And from the side view, their abdomen and buttocks will stick out.
Cervical lordosis :
In a healthy spine, neck shape is wide C, with the curve pointing toward the back of your neck. Cervical lordosis is when your spine in the neck region doesn’t curve as it normally should.
This can mean :
There’s too much of a curve.
The curve is running in the wrong direction, also called reverse cervical lordosis.
The curve has moved to the right.
The curve has moved to the left.
CAUSES :
It’s also called lower cross syndrome. In which muscle surrounding the hip and the spine become tense or weak.
» Achondroplasia – bones do not grow normally, leading to the short stature.
» Spondylolisthesis – the vertebrae in the lower back slip forward.
» Osteoporosis – vertebra become fragile and can easily be broken.
» Obesity – can cause lordosis.
» Kyphosis – can lead to gradually lordosis
» Discitis – the inflammation of inter-vertebral disc
» Benign juvenile lordosis
» Tight lower back muscles
» Excessive visceral fat
» Pregnancy
» Rickets.

POSTURAL ABNORMALITIES
SYMPTOMS :
C-shape back when seen from a lateral aspect, with the buttocks being more prominent
A large gap between the lower back and the floor when lying on one’s back
Pain and discomfort in the lower back
Problems in moving in certain ways.
Lumbar hyperlordosis (anterior pelvis tilt) has an impact on the height of individuals suffering from this medical issue, a height loss of 0.5-2.5 inches is common.
Hyper-lordosis worse’s the symptom’s : These are :
Tingling numbness
electric shock pains
weak bladder bowl control
weakness in lower limb
difficulty maintaining muscle control

MUSCLE IMBALANCE IN LORDOSIS
EXAMINATION :-
Physical examination:
» Palpation determines a spinal abnormality by feel.
» Rang of Motion measure the degree of movement of flexion,extension,lateral bending and spinal rotation.
Neurological Evaluation:
» Assessment of symptoms- pain,numbness,paresthesias,extremity sedation and motor function,muscle spasm,weakness and bowel/bladder changes.
Radiographic:
» Spine AP,PA and lateral view of the spine X-ray taken.
» Cobb’s angel measure degree of the lordosis in AP view of X-ray.
TREATMENT :
Non surgical treatment:
» Medication- NSIADS And Analgesics.
» Physiotherapy- spine strength and flexibility exercise and increase Rang Of Motion.
» Braces- control the curve progression.
» Reduced body weight.
» Back Flexion Muscle Exercise for Lumbar Lordosis.
» Neck Extensor Muscle Strengthening Exercise for Cervical lordosis.
Physiotherapy exercise:

STRETCHING OF LOW BACK MUSCLE

» Anterior-Posterior tilting
» Modified Ball Bridging
» Gluteal stretching
» Cat and Camel
» Hamstring stretching
» Knee to chest
» Trunk Rotation
» Abdominal crunch.
Preventive Measure (Care of Spine ):

There are not exact criteria but few steps help to strengthen spinal muscle and overall functionality of spine :
- Regular Back Flexion Exercise.
- Stretching And Range of motion exercise to avoid stiffness and tightness.
- shoulder shrugging exercise
- Neck Active movements
- Regular Yoga Position
- Straight leg raises (SLR)
- pelvic tilt on a Exercise ball.
- Good Diet

0Comments