However with early diagnosis and medical attention the symptoms of macular degeneration can be reduced and obstructed from further progression. In America, more than 10 million people are diagnosed with macular degeneration which is much greater than the combined count of cataracts and glaucoma eye disease patients.
The macula is the inside back layer of the retina where images are recorded. These recorded images are then sent to the brain via the optic nerve where it is identified or recognized according to the past memory of the brain. The macula is hence responsible for the central vision or straight-ahead vision in the eye that controls your ability to recognize color or faces, seeing objects without waving or distortion, driving vehicle, and reading a book or anything without any difficulty.
The degeneration of the macula usually occurs after the age of 60 that is why this eye disease is also known as Age-related Macular Degeneration or AMD. It is divided into two types known as Dry AMD and Wet AMD depending upon the symptoms. Early-stage symptoms of dry AMD include blurry vision or necessity of more light for reading, difficulty in recognizing faces until a person comes quite closer.
The early-stage symptoms of wet AMD are the wavy appearance of a straight line or an object. Though there is no cure for complete relief of this eye disease but with some lifestyle changes and with antioxidants vitamin intake its progression rate can be reduced for maintaining the remaining vision.
Certain factors that increase a person’s risk of developing macular degeneration include obesity, high blood pressure, smoking, lack of exercise, excessive consumption of simple carbohydrates and high unsaturated fats. So, one can reduce this common aging-related eye health issue by controlling these risk factors from their young age of life in order to have a strong vision throughout life.
Types of Age-related Macular Degeneration
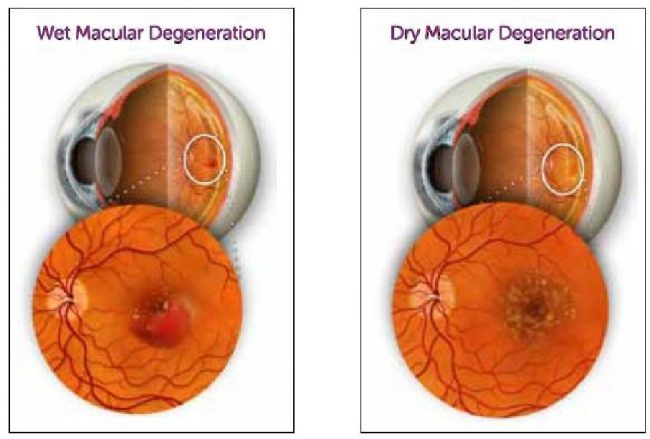 |
| Macular Degeneration |
Macular degeneration which is primarily developed at older stages of life like after the 60s is divided into the following two types.
Dry Age-related Macular Degeneration
In this type of macular degeneration, the light-sensitive cells in the macula break down slowly resulting in the functionality of macula deteriorates with time. This causes a reduction in the central vision. The dry AMD generates in only one eye at first in most of the cases and later on, it may affect the other healthy eye. The actual causes behind the dry age-related macular degeneration are unknown.
The person affected with Dry AMD has to go through its three stages such as an early, intermediate and advanced stage. All these stages may occur either in one or in both eyes. The quantity and features of the drusen existing in your eyes define these three stages. In the case of early AMD, the affected person may either have several small drusen or have few medium-sized drusen. At this particular stage, no symptoms occur nor does the vision loss happen. In the case of intermediate AMD, the affected person may either have several medium-sized drusen or only have one or more large drusen. At this particular stage, the affected person sees a blurred spot in the center of their vision and requires extra light for reading or for doing other tasks.
In the cases of advanced dry AMD stage along with drusen, the breakdown of light-sensitive cells and supporting tissues existing in the central retinal area occur. This condition is called geographic atrophy which can develop blurred spot in the center of vision. As the time progresses this blurred spot may turn into bigger and darker appearance harnessing more of your central vision. At this stage you will experience difficulty in reading a text and recognizing faces until an object or a person is very close to you.
The dry form of AMD is more common than the wet form of AMD. In the case of dry AMD, no blood or fluid leakage occurs into the retinal area also known as retinal swelling or bleeding. Also in this type of AMD, no CNV occurs that is the formation of abnormal new blood vessels under the retina. Over time dry AMD may rapidly convert into wet AMD with the growth of new blood vessels. Also, the dry AMD may advance and can cause vision loss without transforming into wet AMD
Wet Age-related Macular Degeneration
The wet form of AMD occurs due to the abnormal growth of blood vessels from the choroid, the blood vessels layer between the retina and the sclera the outer firm coat of the eye. This abnormal growth may occur under and into the macular portion of your retina. These newly grown blood vessels are also known as choroidal neovascularization or CNV which are very fragile in nature and cause blood or fluid leakage.
As a result of this leakage, the macula displaced from its original or normal place i.e. the back of your eye. This interferes with normal retina’s function leading to blurred central vision. In this case, vision loss may be severe and very rapid. However, in certain cases patients do not experience any changes in their vision in spite of the initiation of CNV.
This is the reason it is suggested to people carrying the risk of CNV to go for periodical eye checkups to diagnose this condition as early as it is possible. CNV of all wet AMD has the ability to cause major visual loss no matter whether there is a significant visual decrease during the diagnosis or not. Once the CNV has occurred in your one eye irrespective of your vision loss, you’re another eye remains at high risk of developing the same changes. Unlike the dry AMD, the wet form of AMD does not have any specific stages. Also, the wet AMD has the potential to cause major vision loss than the dry AMD.
In many cases, people who have the wet form of AMD have already the dry form of AMD at first. All dry AMD patients contain the risk of developing the wet form. However, the dry AMD can advance and may cause vision loss without transforming into the wet form of AMD. Also, the dry form can rapidly turn into the wet form. Anything can happen, there is no definite way at present to identify when and how dry form will convert into the wet form of AMD.
Stages of Age-related Macular Degeneration
The Age-related Macular Degeneration is divided into three stages including-
Early AMD- This is the initial stage of AMD in which the affected person does not notice any vision loss in general. This is the reason why periodical eye examinations are necessary for every individual as this can detect any trouble or issues like AMD in its very early phase. The early AMD is diagnosed by the existence of the medium-sized drusen or yellow deposits beneath the retina.
Intermediate AMD- In the case of the intermediate stage of AMD, some amount of vision loss may be experienced by its patient. However, there will be no significant symptoms even in this stage. In this particular stage, diagnosis is done with a comprehensive eye examination along with specific tests for detecting the larger size drusen or the pigmentation change in the retina.
Late AMD- In this particular stage of AMD there is significant vision loss experienced by its patients.
Causes
The actual cause or reasons behind the growth of AMD or ARMD are unknown but there are certain risk factors that increase the development risk of age-related macular degeneration in a person.
The AMD is more common in older adults or people exceeding their 60s and is the leading cause of vision loss. This eye disease is also correlated with your genes. This means if a person has a family history of AMD then he or she contains a high risk of developing this eye disease in their old age.
Apart from genes, other factors that play a crucial role in causing this severe eye health concern include high blood pressure, high cholesterol level, obesity, smoking, light skin tone, light eye color, being female, being Caucasian and eating lots of saturated fat-rich foods.
Symptoms
Macular degeneration is a chronic disease that means it worsens over time. Initially, the affected person may not notice any vision-related trouble. Also if macular degeneration has affected both eyes at the same time, then also the affected person will not notice any vision changes. However in an advanced stage when the symptoms get worst you may notice following dry macular degeneration signs or symptoms-
- Difficulty in recognizing faces until a person comes closer
- Blurriness
- Distortion of straight lines within your vision field
- Reduction in the central vision
- The necessity of brighter lights in order to read
In the cases of the wet form of macular degeneration, some of its symptoms resemble dry macular degeneration symptoms like reduced central vision and visual distortions. Other than these signs the wet macular degeneration patient may notice following signs or symptoms-
- Hazy vision
- A blurry spot in the field of vision
- Symptoms that worsen rapidly
Both wet and dry form of macular degeneration doesn’t affect your peripheral vision. This eye disease however only affects you from seeing clearly the things that are in front of you but it doesn’t cause total blindness. If you notice any of its symptoms and you contain its risk factors then without further delay immediately visit an eye specialist.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for the complete cure of macular degeneration however, its progression rate can be slowed down with some treatment measures. Also with early diagnosis and treatment, too much of your vision loss can be prevented. Some common treatment measures used for treating macular degeneration includes-
Anti-angiogenesis Drugs
Anti-angiogenesis drugs are prescribed to the macular degeneration patients that obstruct the blood vessels formation as well as leaking from eye vessels that leads to MD. Some anti-angiogenesis medications include pegaptanib (Macugen), bevacizumab (Avastin), ranibizumab (Lucentis) and aflibercept (Eylea). After these medications doses, many people managed to get back their lost vision. You may require this medication treatment multiple times.
Laser Therapy
The abnormal blood vessels formation in your eyes can be blocked with high energy laser light application as it destroys all blood vessels that are growing abnormally.
Photodynamic Laser Therapy
In this particular treatment method, a light-sensitive drug such as verteporfin (Visudyne) is injected in your bloodstream by the doctor. Once the drug is injected, it is absorbed by the abnormal blood vessels that form as a result of macular degeneration. After that, laser light is thrown into your eyes which helps in triggering this injected medication, resulting in the abnormal blood vessels damaged.
Low Vision Aids
These are special devices having specific lenses or electronic systems that help in creating bigger images of the nearby people and objects. These low vision devices are helpful for people who have lost their vision due to macular degeneration.
Apart from these primary treatment techniques medical field researchers are studying for new treatment techniques for macular degeneration. However, these are now in their experimental or progression phase. Some of the experimental treatment measures include-
Submacular Surgery- Surgery is conducted for removing abnormal blood vessels or blood.
Prevention
There is no sure shot way to prevent AMD. However, there are many study reports which suggest that the progression of dry AMD can be reduced with some vital nutrients supplements intake necessary for your eye’s health such as Vitamin A, Vitamin E, zinc, copper, zeaxanthin and lutein. However, it is better that you consult with your doctor before taking these nutrients supplements by own.
Though AMD rarely causes complete vision loss still it can badly impact your daily life routine and activities. So don’t ignore the symptoms of macular degeneration at any cost and visit an eye specialist without making much delay to ensure that you won’t lose any further vision and for preventing the risks of the major damage.

0Comments